Exception Categories
The java.lang.Throwable class acts as the parent class for all objects that can be thrown and caught using the exception-handling mechanisms.
The following figure displays the exception hierarchy of Throwable class.
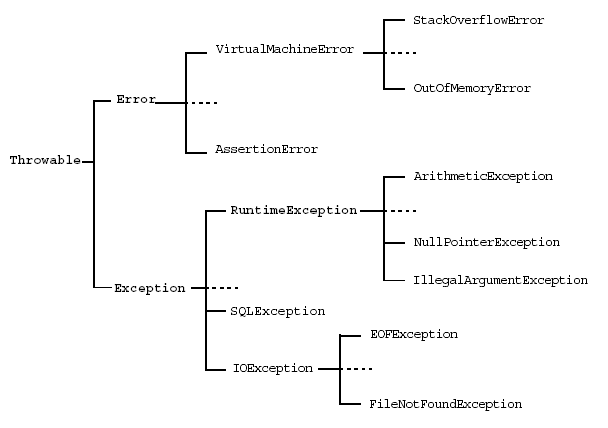
Common Exception Are:
- ArithmeticException
- NullPointerException
- FileNotFoundException
- NumberFormatException
- SecurityException
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
- IllegalArgumentException
- IOException
Method Overriding and Exceptions
When overriding a method that throws exceptions, the overriding method can declare only exceptions that are either the same class or a subclass of the exceptions.
It is permitted to declare that an overriding method throws fewer exceptions than the superclass method, including no exceptions at all
class A
{
public void read() throws FileNotFoundException
{
some code here..
}
}
class B extends A
{
public void read() throws IOException---->WRONG
{
some code here..
}
}
OUTPUT:read() in B can not override read() in A
overrinding method can only throw same or child exception.
overrinding method can only throw same or child exception.
class A
{
public void read() throws FileNotFoundException
{
some code here..
}
}
class B extends A
{
public void read() ---->Correct
{
some code here..
}
}