Array
What Is An Array?
An array is finite ordered set of homogeoneous element.
- Finite :Fixed no of elements
- Ordered :In a sequence or stored in a contiguous block of memory
- Homogeneous : Same type
About Array
- An array is a group of variables of the same data type and referred to by a common name.
- An array consists of a name and the number of elements of the array.
- You can refer to a specific array element by the array name and the element number, which is known as the index number.
- The length of an array is fixed at the time of its creation.
- The following code snippet creates an array named marks: int marks[]=new int[5];
The various types of arrays in Java are:
- One-dimensional arrays
- Multidimensional arrays
1 . One-dimensional arrays
One-dimensional array is a list of variables of the same data type.
Declaration
int marks[]; //Declare array but memory is not allocated yet.
marks=new int[5]; // memory is allocated with new keyword
Or it can be declared in one statement
int marks=new int[5];
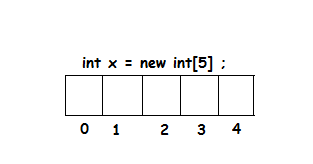
Array index always start from zero.
Initialization
x[0]=10;
x[1]=20;
x[2]=5;
x[3]=50;
x[4]=40;
Array can be initialize at the time of declaration
int x[] = new int[5] {10,20,30,40,50} ;
Simplest Way of declaring and initilaizing array
int x[]={10,20,30,40,50};
String name[]={"Ravi","Mohit","Rahul","Rohit","Arun"};
char grade[]={'a','b','c','d','e'};
Traversing of one-dimentional Array
import java.util.Scanner;
class ArrayTraversing
{
public static vopid main(String...args)
{
int name[]=new int[3];
Scanner ob=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Insert Values In Array");
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
System.out.println("Enter Name");
name[i]=ob.next();
}
System.out.println("Value Are");
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
System.out.println("Name is"+name[i]);
}
}
}
2 . Multidimensional arrays
In Java, multidimensional arrays are actually arrays of arrays.To declare multidimensional arrays, you need to specify multiple square brackets after the array name.
The following code snippet creates a two-dimensional array:
int multiDim[] = new int[3][];
In a multidimensional array, you need to allocate memory for only the first dimension, as shown in the following code snippet:
multiDim[0] = new int[4];
multiDim[1] = new int[4];
multiDim[2] = new int[4];
In addition, when you allocate memory to the second dimension of a multidimensional array, you need not allocate the same number to each dimension.
Declare Twodimensional Array
int x[3][3]=new int[3][3] ;
Initialize Twodimensional Array
x[0][0]=10;
x[0][1]=20;
x[1][0]=5;
x[1][1]=50;
x[2][0]=40;
x[2][1]=40;
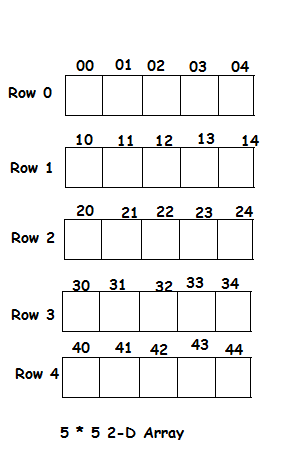
Traversing Two-Dimentional Array
class TraverseTwoDArray
{
public static void main(String... args)
{
//declaring and initializing 2D array
int val[][]={{3,4,5},{2,2,5},{1,2,3}};
//Display 2D array
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
System.out.print(val[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Using Scanner Class
Traversing Two-Dimentional Array
import java.util.Scanner.*;
class TraverseTwoDArray2
{
public static void main(String... args)
{
//declaring and initializing 2D array
int val[][]=new int[3][3];
//Create Scanner Object
Scanner ob=new Scanner(System.in);
//Get User Input
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
System.out.println("Enter Value for "+i+" "+j);
val[i][j]=ob.nextInt();
}
}
//Display 2D array
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
System.out.print(val[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}